MENU
Port forwarding
Once you have fixed the LAN address of the server machine, you should configure the modem router so that it knows to which device on the network to pass any incoming connection from the Internet. This makes it possible to communicate with the server machine outside the LAN.
To do that, first determine, on any computer connected to the network, the address of the default gateway (ie. router) by entering 'ipconfig' on Windows or 'ifconfig' on Ubuntu command-line interface. For some, the address typically looks like 192.168.0.1. Then enter the address into the address bar of any browser to bring out the interface of the modem router, which appears differently for different router models.
On the menu, try to look for 'Port Forwarding' or 'Virtual Server'. For web hosting, once there, create entries to point HTTP (port 80, TCP, internal and external) and HTTPS (port 443, TCP, internal and external) connections to the LAN address of the server machine.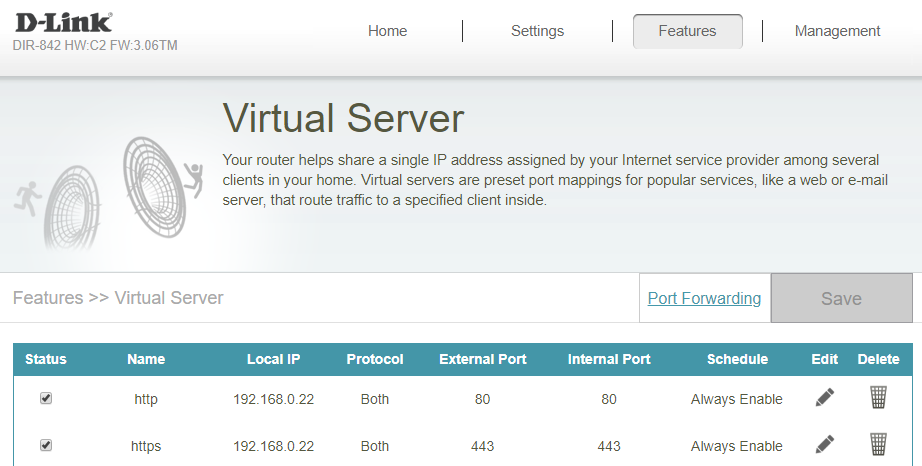
Check that the port is indeed publicly reachable at https://canyouseeme.org/ .
Some modem routers, known as SIM-card modem routers, allow you to connect your devices to the Internet by inserting into the modem router a SIM card issued by a mobile network operator. However, it should be noted that port forwarding is sometimes not permitted by such an arrangement. Hence, if you wish to serve a website to the public, you should generally rely on a conventional ISP (internet service provider).