MENU
Initializing Shaders
10 steps are involved in the use of the vertex and fragment shaders.
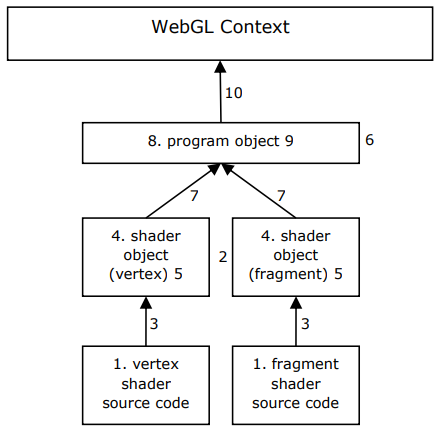
Step 1: Code both shaders using the Shading Language.
The code for a shader can exist as string literals inside a JavaScript or as text content inside the <script> tags outside a JavaScript. We shall see how to do both.
Step 2: Create a shader object for both shaders.
This is done by calling the constructor createShader(type) where 'type' can be VERTEX_SHADER or FRAGMENT_SHADER.
Step 3: Specify the source code for the shader objects.
This is done by calling shaderSource(shader, source). Note that if the sources exist as text inside the <script> tags, they need to be parsed into strings first.
Step 4: Compile the shaders objects.
This is done by calling compileShader(shader).
Step 5: Check the status of the shader compilation.
This is done by calling getShaderParameter (shader,pname). pname can be SHADER_TYPE, DELETE_STATUS, COMPILE_STATUS.
Step 6: Create a program object.
This is done by calling createProgram().
Step 7: Attach both shader objects to the program object.
This is done by calling attachShader (program, shader).
Step 8: Link the program object.
This is done by calling linkProgram(program).
Step 9: Check the status of the linking of the program object.
This is done by calling getProgramParameter(program,pname) where pname can be DELETE_STATUS, LINK_STATUS, VALIDATE_STATUS, ATTACHED_SHADERS, ACTIVE_ATTRIBUTES, ACTIVE_UNIFORMS. The first three return true or false; the last three return an integer.
Step 10: Tell WebGL to use the program.
This is done by calling useProgram(program).
RESETRUNFULL
// /shared/webgl-library.js
function initShaders(gl,vs,fs){
vsScript = (vs.indexOf("main")>0 && vs.indexOf("(")>0)?
vs:document.getElementById(vs).innerHTML;
fsScript = (fs.indexOf("main")>0 && fs.indexOf("(")>0)?
fs:document.getElementById(fs).innerHTML;
vsObj = gl.createShader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER);
fsObj = gl.createShader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER);
gl.shaderSource(vsObj,vsScript);
gl.shaderSource(fsObj,fsScript);
gl.compileShader(vsObj);
gl.compileShader(fsObj);
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(vsObj,gl.COMPILE_STATUS)){
alert("Can't compile the vertex shader.");
}
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(fsObj,gl.COMPILE_STATUS)){
alert("Can't compile the fragment shader.");
return;
}
var p = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(p,vsObj);
gl.attachShader(p,fsObj);
gl.linkProgram(p);
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(p, gl.LINK_STATUS)){
alert("Can't link the shaders-attached program.");
return;
}
gl.useProgram(p);
shaderProgram=p;
return p;
}<!DOCTYPE html><html><head>
<script src="/shared/webgl-library.js"></script>
<script id="vs" type="x-shader/x-vertex">
void main(){
gl_Position = vec4(0.0,0.5,0.0,1.0);
gl_PointSize=30.0;
}
</script>
<script id="fs" type="x-shader/x-fragment">
precision mediump float;
void main(){
gl_FragColor=vec4(1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0);
}
</script>
<script>
function draw_point(){
var canvas = document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var gl = canvas.getContext("webgl");
initShaders(gl,"vs","fs");
gl.clearColor(0.0,0.0,0.0,1.0);
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
gl.drawArrays(gl.POINTS,0,1);
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="draw_point()">
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="500" height="500">
Please use a browser that supports 'canvas'.
</canvas>
</body></html>
Here are some other related functions:
isShader(shader) returns true if 'shader' is a shader object. isProgram(program) returns true if 'program' is a program object.
getShaderInfoLog(shader) returns the information about a shader object as a string. getProgramInfoLog(program) return the information about a program object as a string. validateProgram(program)checks to see if the program is executable given the current states. The information is stored in the program's information log.
deleteShader(shader) deletes a shader object. deleteProgram(program) deletes a program object.
detachShader(program,shader) detaches a shader object from a program object. getShaderSource(shader) returns the source code of the shader object as a string. getAttachedShaders(program) returns an array of shader objects that are attached to 'program'.
bindAttribLocation(program,index, attribute-name) associates a user-defined attribute variable in 'program' with a generic vertex attribute index. If attribute-name refers to a matrix attribute variable, the index refers to the first column, (index+1) refers to the second column, and so on.